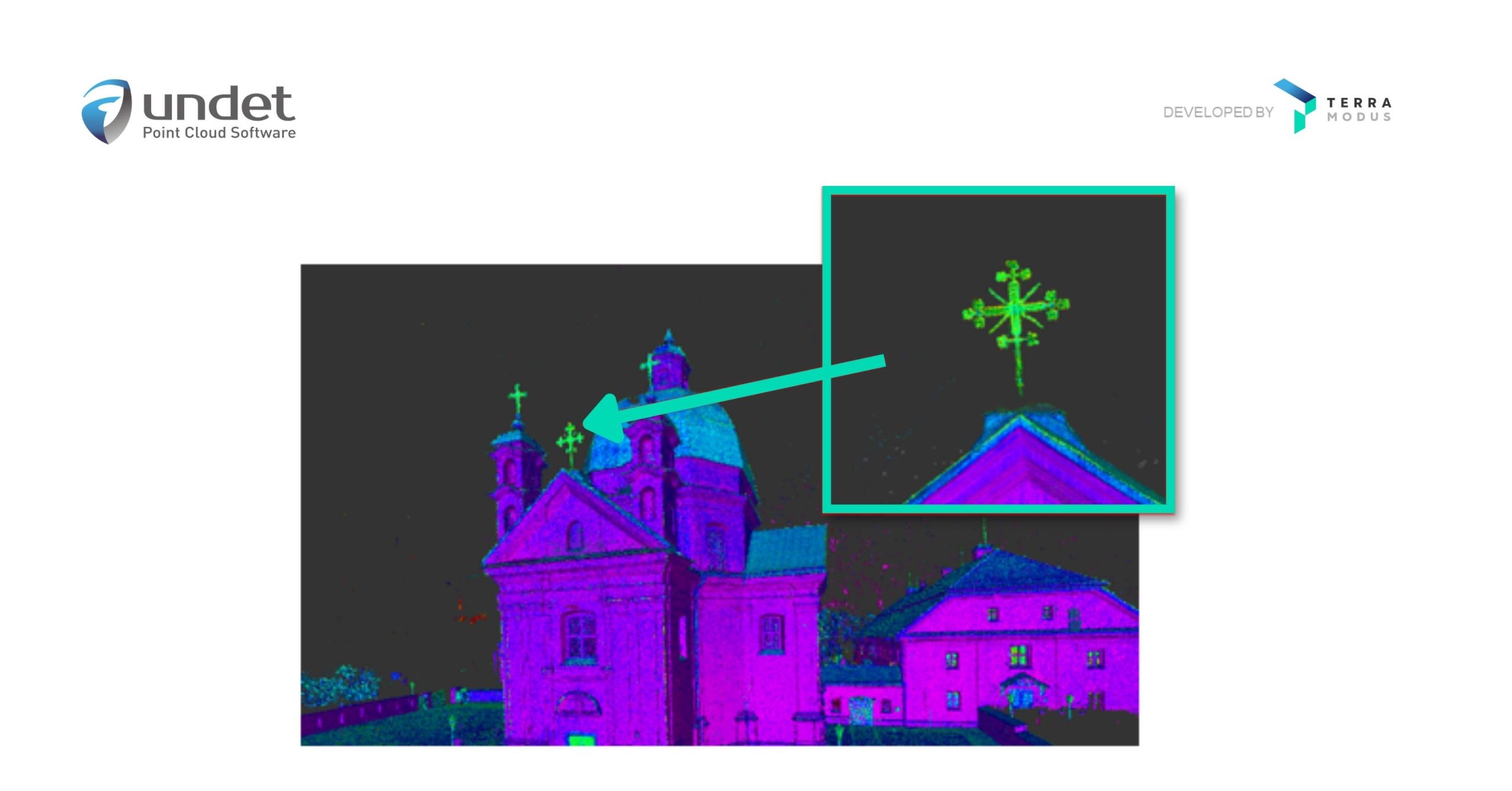
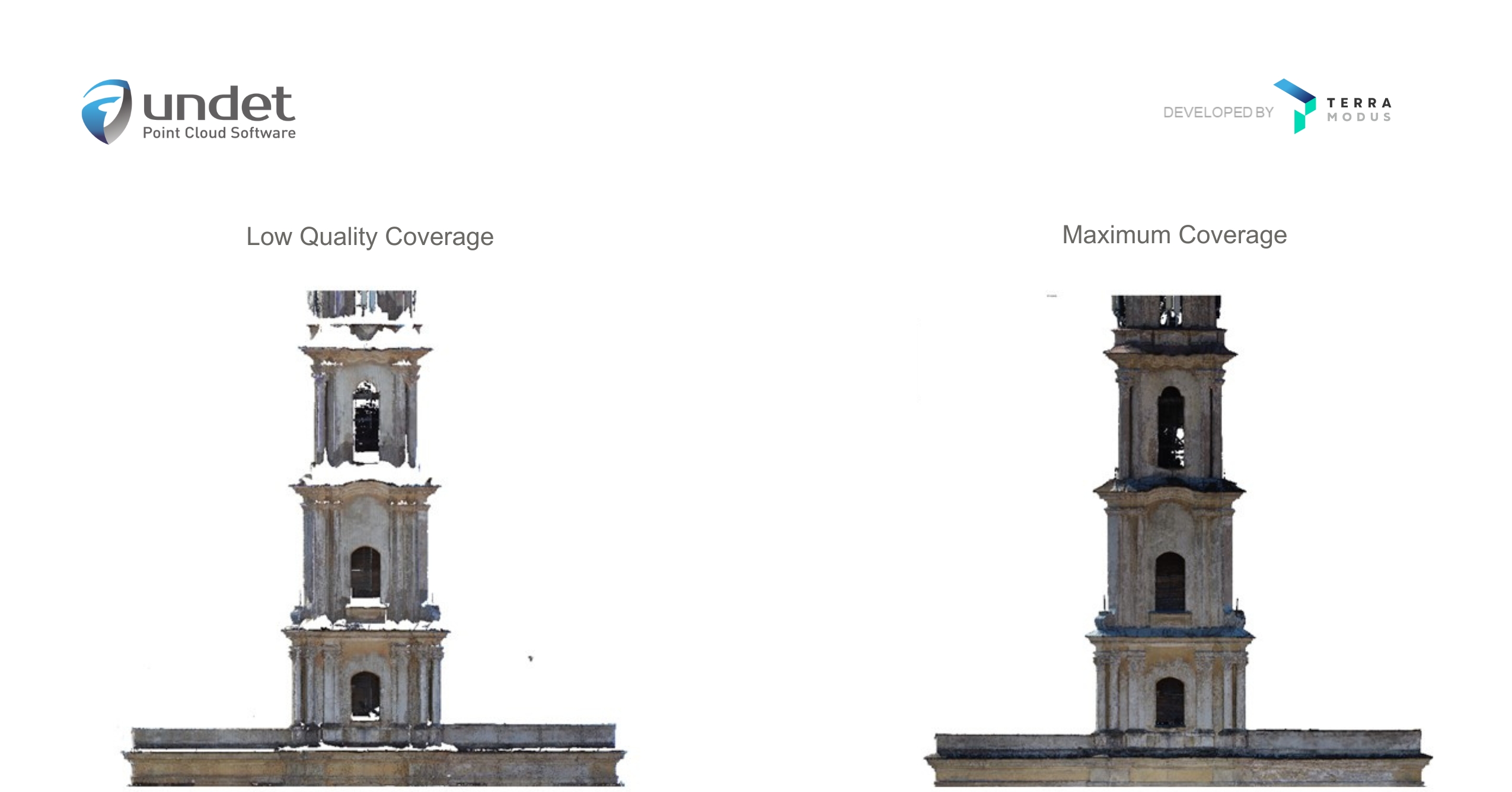
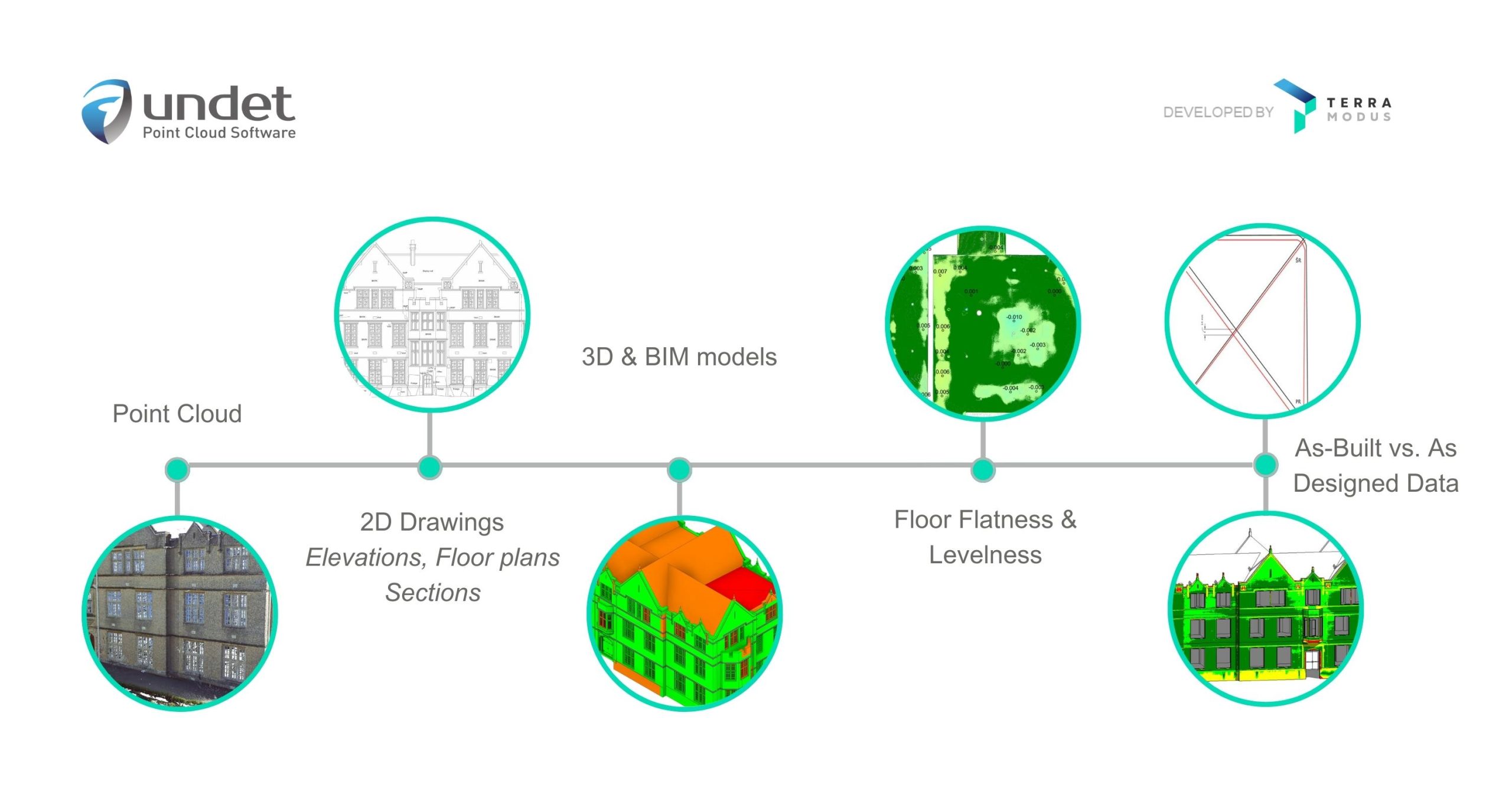
What is point cloud data?
Point cloud data is very simply the data collected via LiDAR or Photogrammetry techniques. 3D point clouds are made up of millions (or sometimes billions) of individual points (hence the name point cloud). Each point containing its X, Y, and Z values along with its orientation (up or down). Some 3D scanners also record colour, which it saves as an RGB value, as well as intensity.
How is point cloud data processed?
Once you have collected your point cloud scan data via LiDAR or photogrammetry, there is still quite a bit of work to do in order to turn it into a finished 3D model that you can send to your clients. This is where point cloud processing comes in.
Using point cloud software such as Undet, you are able to import and work on this data in CAD software such as AutoCAD, Revit, SketchUp or Ares Commander. The software helping you to process your point cloud and turn it into your desired result, be it a 3D model, 2D plans or BIM deliverables.
Essentially point cloud data is processed by the software based on what it is you want. For example, you may have scanned an entire building, but for the particular project you are working on, you only require data on the roof. Point cloud software allows you to take out and work with only the data points you need. Allowing you, in this case, to accurately see, measure and model the current roof – and use that information to create a 3D model for a new roof or detailed 2D plans for renovations or documentation purposes.
What is point cloud software?
Point cloud software is software that helps you to import and work with point cloud data. Point cloud software, such as Undet usually comes in the form of plugins and extensions that are used in CAD software such as AutoCAD, Revit, ARES Commander and SketchUp.
Because both free and paid point cloud software is available, it therefore comes down to your specific requirements and how much you can afford to spend. As you might expect, paid software often has much more functionality and is more optimized for working with point cloud data than free alternatives.
What additional features does point cloud software provide?
Point cloud software provides additional features and functionality that is specially tailored to working with points cloud data sets. As a simple example, point cloud software such as Undet, makes importing point cloud data much quicker, meaning you can get to work on your new project more quickly.
In addition, point cloud software generally offers a suite of other tools that make working with point clouds, meshes and 3D models easier and quicker. Some point cloud plugins and extensions also have tools that help you to check the accuracy of work. These quality assurance tools, potentially saving you a lot of time and money on costly reworks.
What can you do with point clouds?
Point clouds allow us to digitize an existing object, and make accurate 3D models or 2D drawings from it. This has applications throughout the entire life cycle or a building, from design, through to construction, renovation and operation.
3 potential applications of point clouds are:
- To carry out assessments and measurements when expanding or upgrading facilities and infrastructure.
- To design and present your ideas and see how they will fit and affect an existing environment.
- To document and archive the existing structure before changing or demolishing it.
Very simply, before we can change, rebuild or renovate something, we must assess and measure the current situation – this is exactly what point clouds allow us to do.
What is the difference between a point cloud and a mesh?
The basic difference between a mesh and a point cloud is that a mesh is a collection of interconnected triangles or polygons that come together to make a solid 3D surface, while a point cloud is a 3D representation made up of thousands or millions of dots (the points).
Meshes are used because they provide an efficient and lightweight way to represent complex 3D shapes. They can also be easily manipulated and textured in point cloud software. On the contrary, point clouds are usually less efficient when it comes to processing and rendering because they require more computational resources to represent a 3D shape accurately. To put this into some perspective, mesh models can reduce the size of point cloud files by as much as 90%. Making meshes much quicker to work with and easier to share with colleagues.
This is why point clouds are often converted into a 3D mesh, which can then be used in CAD software to create 3D models, 2D plans and BIM deliverables.
What is the difference between LiDAR and Photogrammetry?
The difference between Lidar and Photogrammetry is basically the way in which each creates a point cloud and what technology it uses to do so. Whereas laser scanners use LiDAR technology, photogrammetry uses photos taken by high-definition cameras to deliver a similar result. But, to understand these differences in more detail and discover which option is best for you, we must first learn a little each.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR, which stands for “Light Detection And Ranging”, is a technology that uses lasers to build up a 3D image of an object or area being scanned. It does this by sending out pulses of light and measuring how long it takes for these to return and how strong they are. Each individual measurement coming together with thousands or millions of others to create a 3D point cloud. The use of lasers in this technology is also why you will commonly hear the term laser scanning a lot in this industry.
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry uses photographs taken by high-resolution RGB cameras to create a 3D image of an area or object. This is possible because the photos are taken deliberately to overlap with one another and from various different vantage points in such a way that a 3D image can be generated from the 2D photographs.
LiDAR or Photogrammetry: Which is best for you?
This is an important question. If you want the most accurate point cloud laser scanning measurements and results possible then opt for LiDAR. However, photogrammetry offers photo-realistic results, and costs less.